National Science Board Reports a Need for More Support of STEM Talent

Send us a link



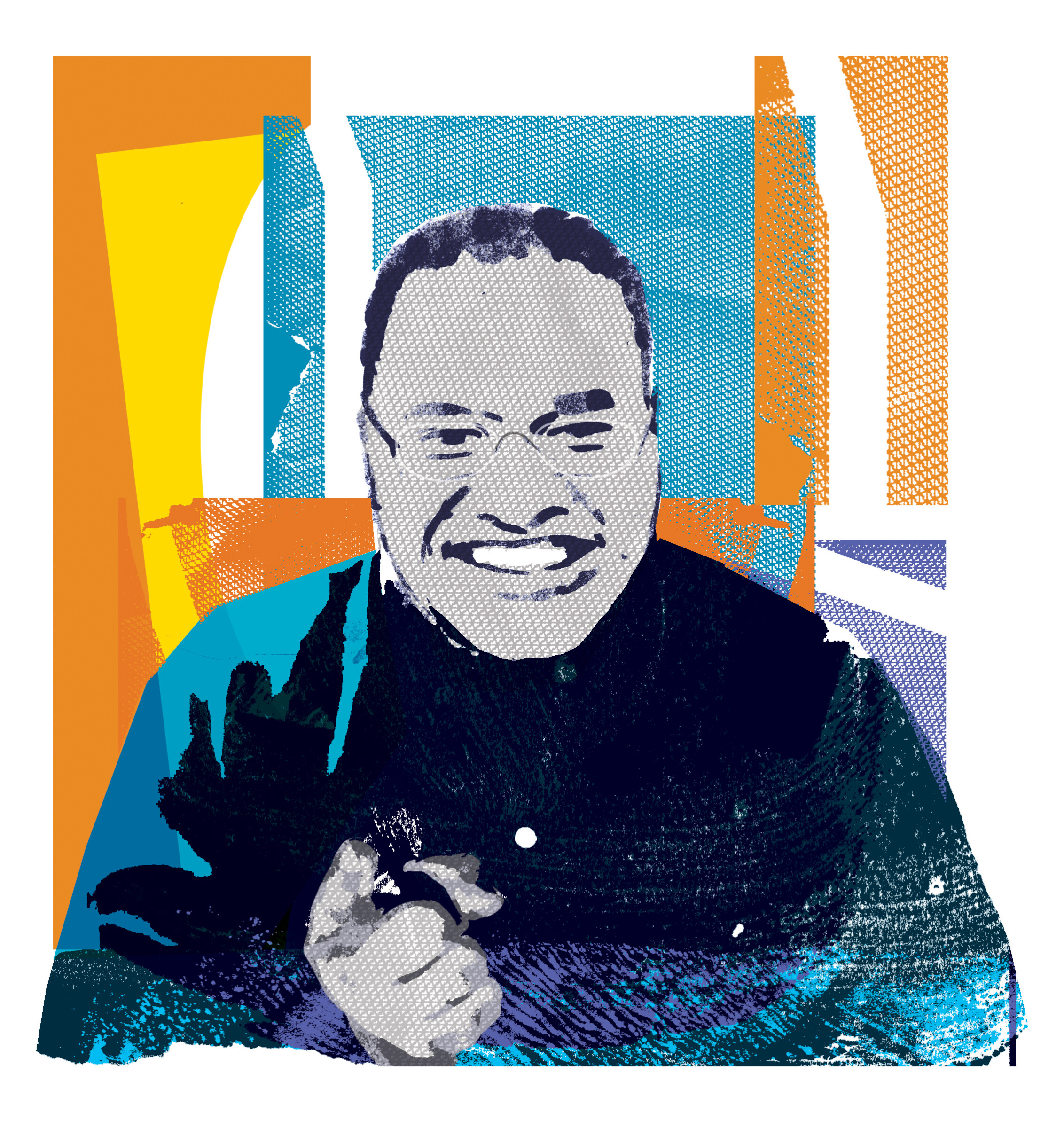
Mathematician and educator Freeman A. Hrabowski III talks about the importance of the humanities, culture change in academia, and much more. He has led groundbreaking efforts to increase diversity in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields throughout his career. As president of the University of Maryland, Baltimore County (UMBC) for three decades, Hrabowski transformed a regional commuter school into a top-tier research university.

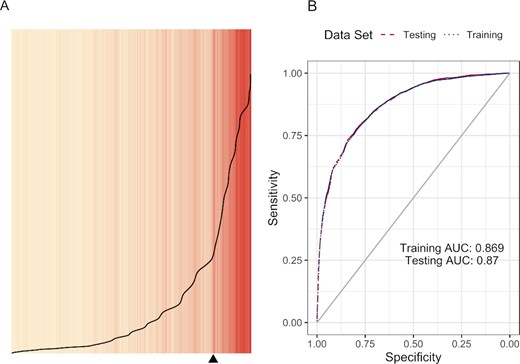
This study found that the association between low performance in an introductory STEM class and failure to obtain a STEM degree is stronger for underrepresented minority (URM) students than for other students, even after controlling for academic preparation in high school and intent to obtain a STEM degree.
The recently passed CHIPS and Science Act promises billions of dollars in funding to support science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) research and production at government agencies, private companies, and colleges and universities across the U.S. It also includes provisions to increase diversity in STEM education and the workforce and to promote socioeconomic development for underserved communities.

Early-career scientists should have a say in developing the policies that can help them in the short term as well as benefit the scientific system in the long term, writes Adriana Bankston.
Within a year of the shutdowns caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, virtual meetings transformed from an auxiliary service to an essential work platform for hundreds of millions of people worldwide. Universities rapidly accelerated adoption of virtual platforms for remote conferences, classes, and seminars amidst a second crisis testing institutional commitment to the principles of equity, diversity, and inclusion. To address these concerns, we began the Diversity and Science Lecture series (DASL), a cross-institutional national platform where junior life scientists present personal stories, professional progress, and advice for their peers.

Universities and graduate institutions must adapt to meet the increasing demand for STEM laborers in non-academic sectors and provide relevant and robust training to their students.
For women in science and engineering, careers in the academic world tend to appeal for their flexibility and potential to make a difference.
With today's existing translation tools to overcome language barriers, global collaboration should not be a major feat for researchers. However, through the COVID-19 pandemic, articles published in Chinese journals focusing on important aspects of the disease were never cited by English journals.

Help us increase the visibility of women in STEM and inspire the next generation of women scientists. Join us in writing Wikipedia biographies of women in STEM in October and November.
Mother in Science is launching the first global survey to measure the impact of having children on career progression, scientific productivity and career choices of women in STEMM, and to identify the specific motherhood-related factors driving gender imbalance in STEMM employment.

Table of Contents 1. "There is no evidence of racism in STEM."2. "Don't politicize STEM! Stick to the science, not social issues."3. "I'm not a racist, so I don't need to do anything."4. "I only hire/award/cite based on merit; I do not need to consider race."5. "There just aren't as many BIPOC who want to…
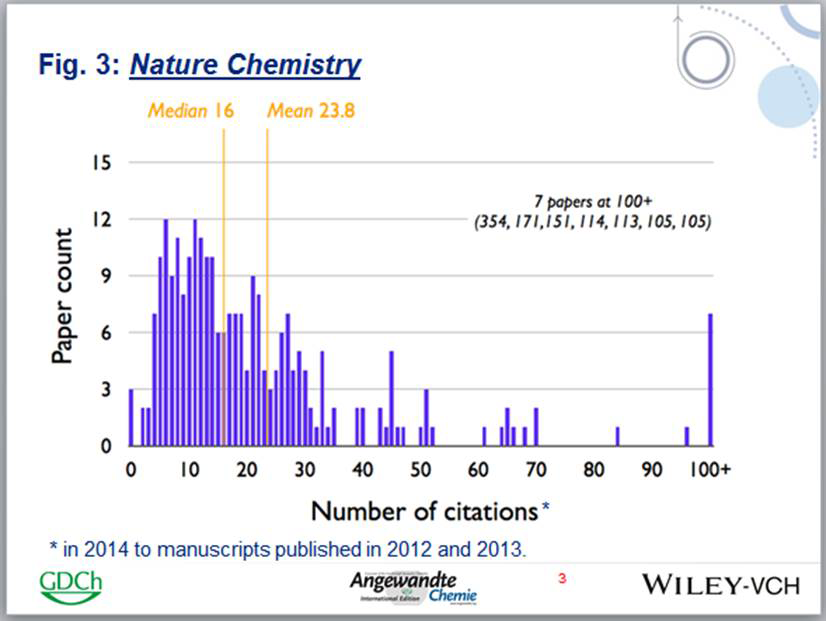
In this article, potentially high-impact policy changesare outlined that build upon existing mechanisms for research funding and governance and that can be rapidly implemented to counteract barriers facing women in science. These approaches must be coupled to vigorous and continuous outcomes-based monitoring, so that the most successful strategies can be disseminated and widely implemented.
