Can Better Biotech Finally Replace Lab Animals?
Replacing research animals with tools that better mimic human biology could improve medicine.

Send us a link
Replacing research animals with tools that better mimic human biology could improve medicine.

For far too long, medicine has ignored the valuable insights that patients have into their own diseases.
As the United Kingdom braces for a sharp fall in living standards, a bioarchaeologist and a paediatrician discuss what the past can reveal about the social forces that shape modern health crises.

The historical lack of racial representation in dermatology textbooks isn't just a problem in countries with majority white populations, but across the globe.

A look into the value of providing plain language summaries in research papers, and the standards created for doing so.
Global travelers, whether tourists or secret agents, are exposed to infectious agents. We hypothesized that agents pre-occupied with espionage and counterterrorism may, at their peril, fail to correctly prioritize travel medicine.
Osteoarthritis is a crippling, incurable disease. But scientists behind a new large-scale study say their findings could help pave the way to a cure.

Health research is based on trust. Health professionals and journal editors reading the results of a clinical trial assume that the trial happened and that the results were honestly reported. But about 20% of the time, said Ben Mol, they would be wrong.

University of Queensland researchers have found a bacteria-killing compound in the toxins of mottled cup moth caterpillars

By bringing rigorous review and editorial oversight to clinical preprints, eLife hopes to make peer-reviewed preprints a currency of trust in medicine.
Australian scientists develop a microscope that works with 35% more clarity, raising hope for improvements in medical imaging.
Approaches include tailored nanoparticles, chimeric proteins, virus cocktails.
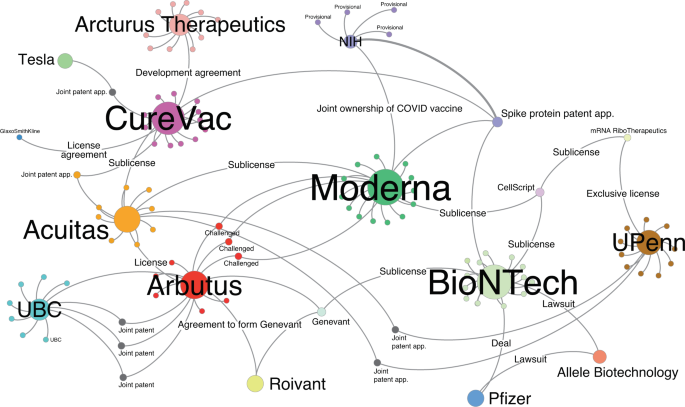
A preliminary network analysis highlights the complex intellectual property landscape behind mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines.
As a bioengineer, Linda Griffith once grew a human ear on the back of a mouse. Now she is reframing endometriosis as a key to unlocking some of biology's greatest secrets.

Results from a long-term study of 8001 people suggest disrupted sleep is linked to cardiovascular disease and mortality - in women more than men.

For many years and increasingly in the last year, the JAMA Network journals have published many important articles addressing disparities and racism in medical education, research, and health care and highlighting initiatives to help address deep-rooted inequities.

A new oath asks physicians to eliminate their personal biases, combat disinformation to improve health literacy and be an ally to minorities and other underserved groups in society.