What is Replication?
This perspective article proposes that the answer shifts the conception of replication from a boring, uncreative, housekeeping activity to an exciting, generative, vital contributor to research progress.
Send us a link
This perspective article proposes that the answer shifts the conception of replication from a boring, uncreative, housekeeping activity to an exciting, generative, vital contributor to research progress.
Citation metrics are widely used and misused. This Community Page article presents a publicly available database that provides standardized information on multiple citation indicators and a composite thereof, annotating each author according to his/her main scientific field(s).
Happy Open Data Day 2019! It's that special day of the year again! Well, every day should be Open Data Day, but today lots of motivated folk come together around the world to remind us all why Open Data, Open Science, and sharing of data and science in general is better for everyone. Better for reuse, better for tracking public money flows, better for open mapping and development, and also, lest we lost sight, better for the researcher who produced the data! Why better for the researchers who generated the data? Better because the value add from sharing is multifold. Others can reuse and reanalyse your data. If you've placed the data in a repository with a persistent identifier, you'll get attributed when they are reused and you can get credit for this - and even citations. What may not be immediately obvious is that taking a little bit of time to ensure your data are 'sharable' is good practise that ensures that when you want to use
Scientists waste substantial time writing grant proposals, potentially squandering much of the scientific value of funding programs. This Meta-Research Article shows that, unfortunately, grant-proposal competitions are inevitably inefficient when the number of awards is small, but efficiency can be restored by awarding funds through a modified lottery, or by weighting past research success more heavily in funding decisions.
In this Perspective, a group of national funders, joined by the European Commission and the European Research Council, announce plans to make Open Access publishing mandatory for recipients of their agencies' research funding.
An introductory course that guides students towards a reproducible science workflow.
In order to better serve authors, an agreement between the two organizations outlines broader use of bioRxiv for preprints of papers submitted to PLOS journals.

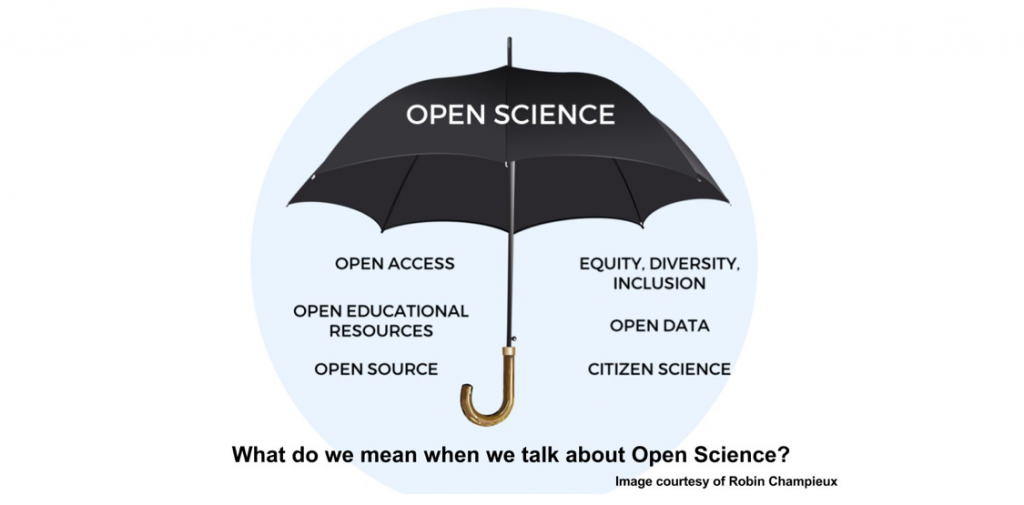
Some answers to the main challenges in moving toward Open Science.
Scientific research can be a cutthroat business, with undue pressure to publish quickly, first, and frequently. PLOS Biology is now formalizing a policy whereby manuscripts that confirm or extend a recently published study are eligible for consideration.
This Perspective article argues that universities should take action to support open scholarship that benefits society and to return to their core missions of knowledge dissemination, community engagement, and public good.
More than 26 percent of papers identified as systematic reviews or meta-analyses contained spin. This figure rose to up to 84 percent in papers reporting on nonrandomised trials.
Funder reflections on the Open Science Prize.
Unencumbered dissemination of scientific research depends on a fair Internet.

Introducing Wide-Open, a system that identifies large number of overdue datasets.
Remember the Kardashian index? That was Neil Hall's 2014 tongue-in-cheek(ish) dig at science Twitter and "Science Kardashians" - scientists with a high Twitter-follower-to-citation ratio.

Consider biomedical preclinical and clinical research, in which the trusted service involves the exchange of papers, data, software, reagents, and so on.
Computational thinking and techniques are so central to the quest of understanding life that today all biology is computational biology.
Ambra is an innovative Open Source platform for publishing Open Access research articles. It provides features for post-publication discussion and versioned articles that allows for a “living” document around which further scientific discoveries can be made. The platform is in active development by PLOS (Public Library of Science) and is licensed under the MIT License.
A set of best practices for scientific software development, based on research and experience, that will improve scientists' productivity and the reliability of their software.
Searching Google Scholar in 16 languages revealed that 35.6% of 75,513 scientific documents on biodiversity conservation published in 2014 were not in English.
A current debate about conflicts of interest related to biomedical research is to question whether the focus on financial conflicts of interest overshadows “nonfinancial” interests that could put scientific judgment at equal or greater risk of bias.
Seeking to accelerate research advances and reimagine its role in the community, the Montreal Neurological Institute (Neuro) announced in the spring of 2016 that it is launching a five-year experiment during which it will adopt Open Science—open data, open materials, and no patenting—across the institution.
Women are still underrepresented in terms of authorships, including first and/or last authorships (whichever is more prestigious), coauthorships, and in the granting of scientific prizes.
Researchers acting to maximise their fitness should spend most of their effort seeking novel results and conduct small studies that have only 10%–40% statistical power. As a result, half of the studies they publish will report erroneous conclusions. Current incentive structures are in conflict with maximising the scientific value of research; we suggest ways that the scientific ecosystem could be improved.
An empirical analysis of researchers’ publications reveals that females have fewer distinct coauthors yet have a lower chance of repeating previous coauthors than their male counterparts.
For some time now PLOS has discussed new initiatives designed to accelerate research communication.
